Understanding Generalization in Deep Learning: Practical Business Solutions
Deep neural networks exhibit behaviors such as benign overfitting, double descent, and successful overparametrization. These phenomena can be explained through established frameworks and are not exclusive to neural networks. By understanding these concepts, businesses can leverage AI effectively.
Key Principles
A researcher from New York University introduces the concept of “soft inductive biases.” This approach prefers simpler solutions while allowing flexibility in hypothesis space. This principle applies not just to deep learning but also to various model types, emphasizing that deep learning is not fundamentally different from other methodologies.
Inductive Biases
Inductive biases typically restrict hypothesis space to enhance generalization. For example, convolutional neural networks impose hard constraints to improve performance. In contrast, soft inductive biases guide the hypothesis space without excluding alternative solutions. This flexibility is crucial for addressing complex data structures.
Real-World Applications
To utilize AI effectively, businesses should:
- Identify areas where processes can be automated.
- Determine key performance indicators (KPIs) to measure the impact of AI investments.
- Select customizable tools that align with business objectives.
- Start with a small AI project, gather data on its success, and gradually expand usage.
Understanding Overfitting and Generalization
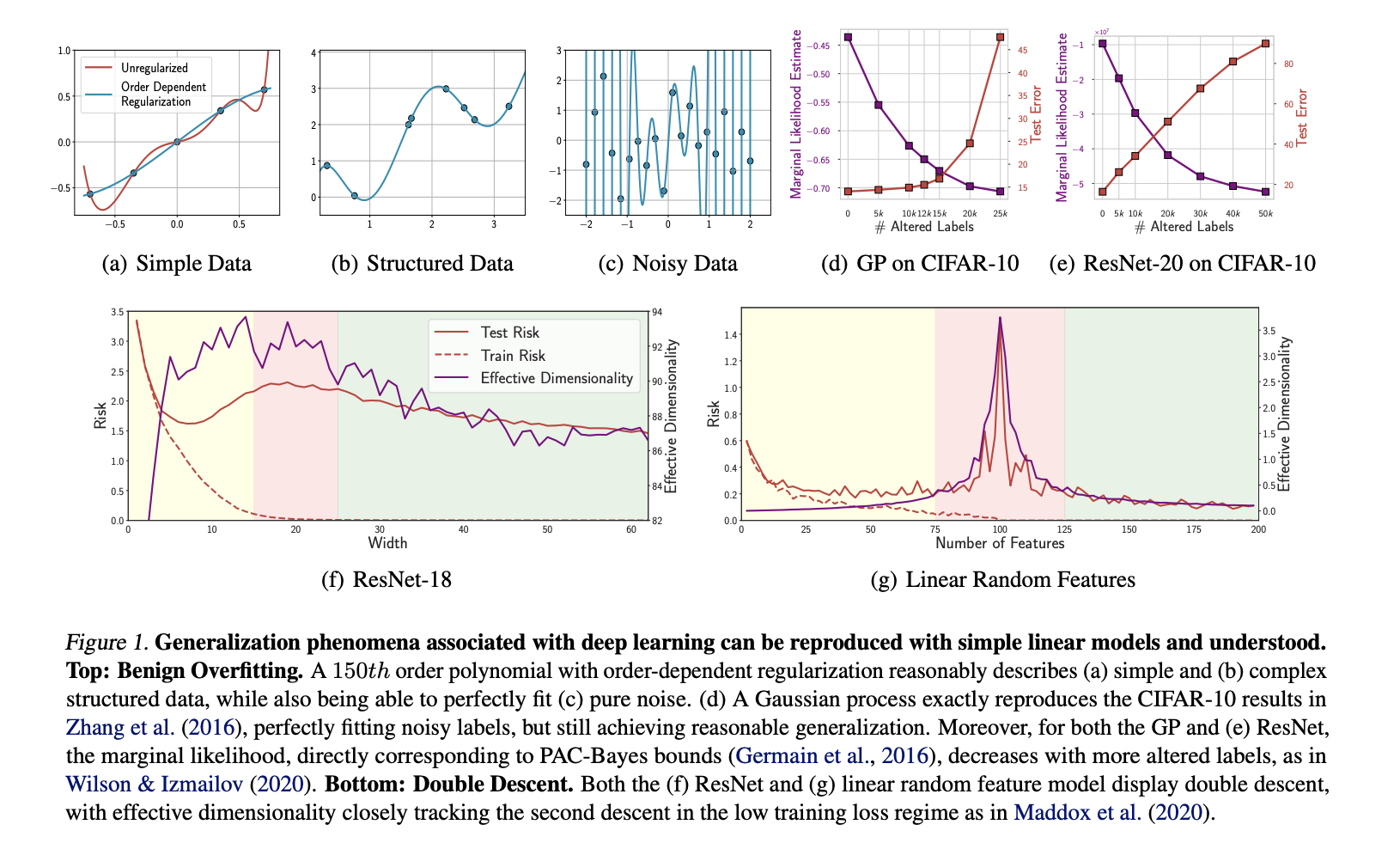
Benign overfitting allows models to fit noise while still performing well on structured data. For instance, convolutional neural networks can accurately classify images even when trained on random labels. This contradicts traditional frameworks but highlights the potential of deep learning.
Double Descent Phenomenon
Double descent describes a pattern where generalization error decreases, increases, and then decreases again as model complexity grows. This behavior can be tracked using PAC-Bayes bounds, providing insights for practical applications in model selection and training.
Conclusion
Overparametrization, benign overfitting, and double descent offer valuable insights for businesses adopting AI. These concepts challenge conventional wisdom but can be explained through established frameworks. By understanding these phenomena, organizations can make informed decisions about AI implementation.
For further guidance on managing AI in business, feel free to contact us at hello@itinai.ru or connect with us on Telegram, X, and LinkedIn.
























