Enhancing AI Reliability in Healthcare
Introduction
As large language models (LLMs) gain traction in healthcare, ensuring that their outputs are backed by credible sources is crucial. Although no LLMs have received FDA approval for clinical decision-making, advanced models like GPT-4o, Claude, and MedPaLM have shown superior performance on standardized exams, outperforming human clinicians. These models are currently used in various applications, including mental health support and diagnosing rare diseases. However, their tendency to produce unverified or inaccurate information poses significant risks, particularly in medical contexts.
Challenges in Source Attribution
Despite advancements in LLM technology, such as instruction fine-tuning, challenges remain in ensuring that the references provided by these models genuinely support their claims. Recent studies have introduced datasets to evaluate LLM source attribution, but these methods often rely on time-consuming manual evaluations. Innovative approaches, like those utilized in ALCE and FactScore, have emerged to assess attribution quality more efficiently, yet the reliability of citations remains a concern.
SourceCheckup: A Solution for Reliable Attribution
Researchers at Stanford University have developed SourceCheckup, an automated tool aimed at evaluating how accurately LLMs support their medical responses with relevant sources. In their analysis of 800 questions, they discovered that 50% to 90% of LLM-generated answers lacked full support from cited sources. Notably, even models with web access struggled to consistently provide reliable responses.
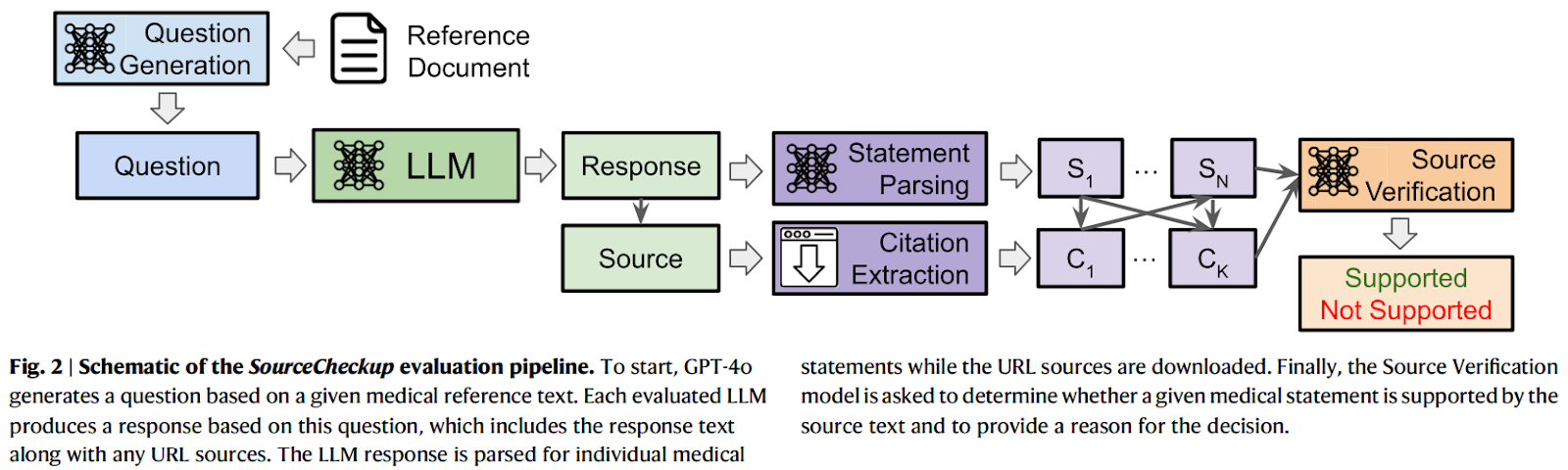
Study Methodology
The SourceCheckup study involved generating medical questions from two sources: Reddit’s r/AskDocs and MayoClinic texts. Each LLM’s responses were assessed for factual accuracy and citation quality. The evaluation included metrics such as URL validity and support levels, validated by medical experts. The results highlighted significant gaps in the reliability of LLM-generated references, raising concerns about their readiness for clinical use.
Key Findings
- 50% to 90% of LLM responses lacked full citation support.
- GPT-4 showed unsupported claims in about 30% of cases.
- Open-source models like Llama 2 and Meditron significantly underperformed in citation accuracy.
- Even with retrieval-augmented generation (RAG), GPT-4o only supported 55% of its responses with reliable sources.
Recommendations for Improvement
To enhance the trustworthiness of LLMs in medical contexts, the study suggests several strategies:
- Train or fine-tune models specifically for accurate citation and verification.
- Utilize automated tools like SourceCleanup to edit unsupported statements, improving factual accuracy.
- Implement continuous evaluation processes to ensure ongoing reliability in medical applications.
Conclusion
The findings from the SourceCheckup study highlight ongoing challenges in ensuring factual accuracy in LLM responses to medical queries. As AI continues to evolve, addressing these issues is essential for building trust among clinicians and patients alike. By focusing on improving citation reliability and verification processes, the healthcare industry can better leverage AI technologies while minimizing risks associated with misinformation.
For further insights into how artificial intelligence can transform your business processes, consider evaluating your current operations for automation opportunities, identifying key performance indicators (KPIs), and starting with small pilot projects to measure effectiveness before scaling.























