Transforming Tactile Sensing with AI: Practical Business Solutions
Understanding Tactile Sensing Technology
Tactile sensing is essential for intelligent systems to effectively interact with the physical environment. Technologies like the GelSight sensor provide detailed information about contact surfaces by converting tactile data into visual images. However, a significant challenge arises from the lack of transferability between different tactile sensors, which can lead to inconsistent performance when models trained on one sensor are applied to another.
Challenges in Current Tactile Sensing Approaches
The primary issues with existing vision-based tactile sensors include:
- Variability in tactile signals due to differences in sensor design and manufacturing.
- The need for large datasets to train models, which limits flexibility and generalization to unseen sensors.
- Inadequate methods for transferring knowledge across sensor types, often treating them as fixed categories.
Innovative Solutions: Sensor-Invariant Tactile Representations (SITR)
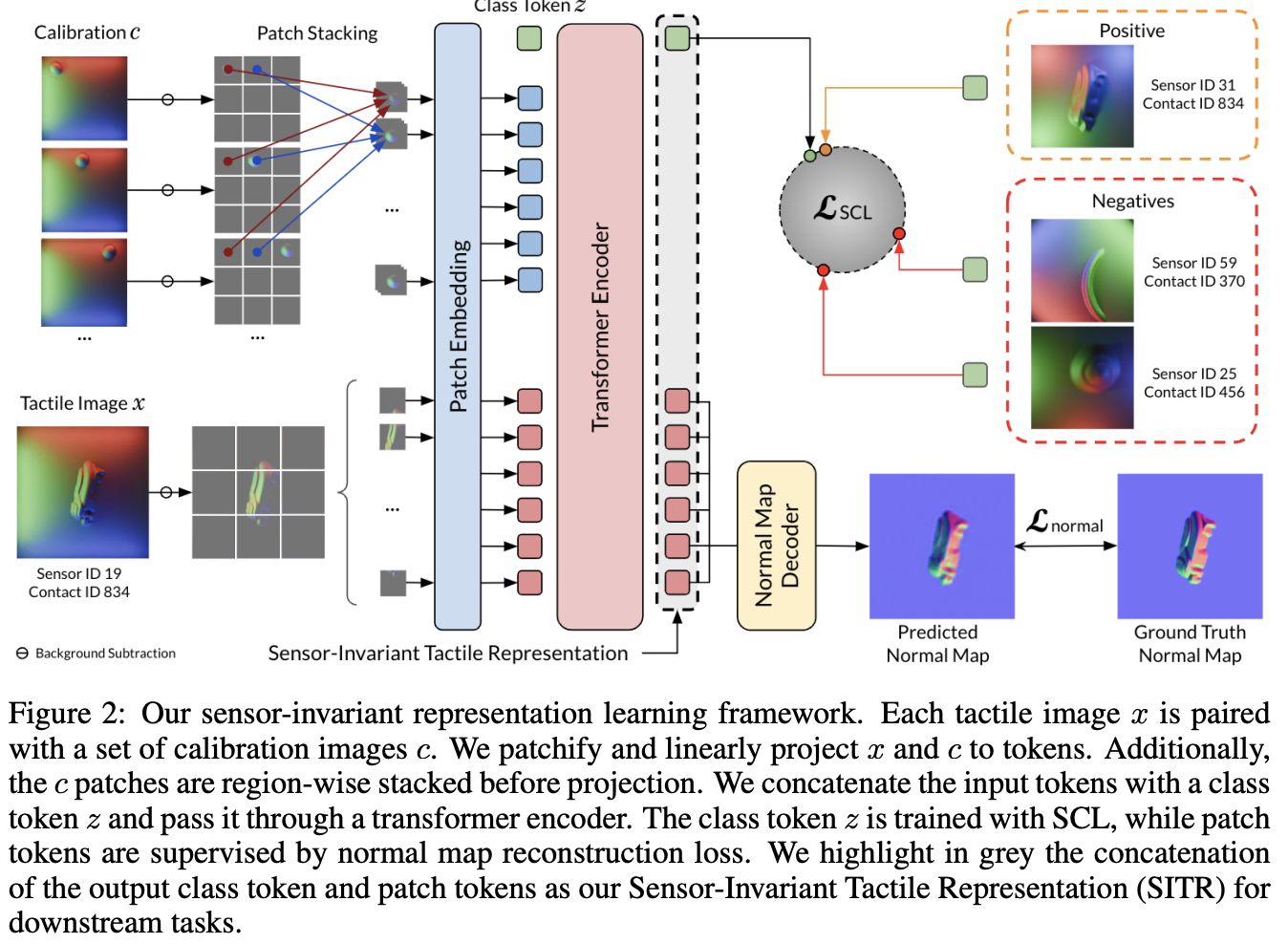
Researchers from the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign have introduced the Sensor-Invariant Tactile Representations (SITR) framework. This innovative approach allows for the transfer of tactile representations across various vision-based sensors without the need for retraining. Key components of SITR include:
- Calibration Images: Easy-to-acquire images that characterize individual sensors.
- Supervised Contrastive Learning: A method that emphasizes geometric aspects of tactile data, enhancing the model’s ability to generalize.
- Large-Scale Synthetic Datasets: A dataset containing 1 million examples across 100 sensor configurations to improve training effectiveness.
Case Study: Performance of SITR
In practical applications, SITR has demonstrated superior performance in object classification and pose estimation tasks compared to existing models. For example:
- In object classification tests, SITR outperformed all baseline models when applied across different sensors.
- In pose estimation tasks, SITR achieved a 50% reduction in Root Mean Square Error compared to traditional methods, showcasing its robustness and effectiveness.
Implications for Businesses
The advancements in tactile sensing technology through SITR present significant opportunities for businesses, particularly in robotics and automation. By adopting this technology, companies can:
- Enhance robotic manipulation capabilities, leading to more efficient operations.
- Reduce the costs associated with sensor-specific model training.
- Accelerate the implementation of tactile sensing technologies across various applications.
Conclusion
The introduction of Sensor-Invariant Tactile Representations marks a pivotal advancement in tactile sensing technology, enabling seamless transferability across different sensors. This innovation not only addresses existing challenges but also opens new avenues for businesses to leverage AI in enhancing their operational efficiency and capabilities. By embracing these advancements, organizations can stay at the forefront of technological progress and drive significant value in their operations.
For further insights on integrating AI into your business processes, feel free to reach out to us at hello@itinai.ru.

























