Transforming Software Maintenance with LocAgent
Introduction
The maintenance of software is essential to the development lifecycle, where developers regularly address existing code to fix bugs, implement new functionalities, and enhance performance. A key aspect of this process is code localization, which involves identifying specific areas in the code that require updates. As software projects grow in scale and complexity, code localization has become increasingly important.
The Challenges of Code Localization
Identifying Code Changes
One major challenge in software maintenance is accurately recognizing which parts of the code require modifications based on user feedback or feature requests. Often, user reports highlight symptoms without specifying the underlying code issues, complicating the link between descriptions and necessary code changes.
Limitations of Traditional Methods
Conventional approaches to code localization typically rely on dense retrieval models or agent-based strategies. Dense retrieval methods require embedding complete codebases into a searchable format, which becomes unwieldy for large repositories. Meanwhile, agent-based models simulate user exploration of code but struggle to understand complex relationships between code elements. As a result, these methods often fail to efficiently resolve bugs, leading to longer development cycles.
Introducing LocAgent
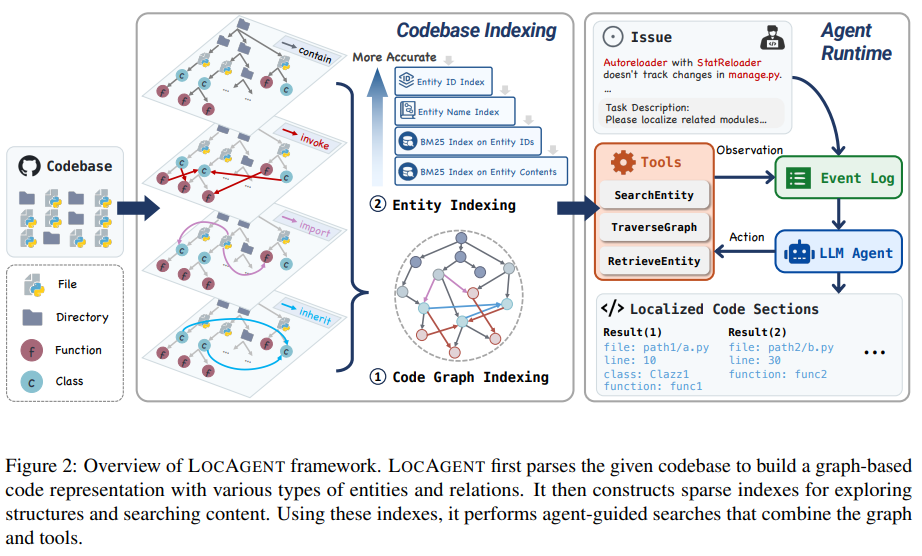
A collaborative research effort from Yale University, USC, Stanford University, and All Hands AI has produced LocAgent, a revolutionary framework that employs graph-based techniques for code localization. Unlike previous methods that rely on surface-level matching, LocAgent converts codebases into directed heterogeneous graphs, capturing the intricate relationships between different code components.
How LocAgent Works
LocAgent structures code into graphs with nodes representing directories, files, classes, and functions while edges capture relationships like function calls and class hierarchies. This comprehensive graph enables the agent to reason across various levels of code abstraction, making it easier to trace and modify relevant sections of code.
Performance and Results
Real-Time Indexing and Accuracy
LocAgent demonstrates rapid indexing capabilities and supports real-time application for developers. The researchers refined two open-source models, Qwen2.5-7B and Qwen2.5-32B, achieving notable results on benchmark datasets. For instance, LocAgent attained an impressive 92.7% file-level accuracy on the SWE-Bench-Lite dataset, outperforming other models, including Claude-3.5, which achieved only 86.13%.
Cost-Effectiveness
Notably, the smaller Qwen2.5-7B model provides performance comparable to expensive proprietary solutions while costing just $0.05 per example—significantly lower than $0.66 for Claude-3.5.
Key Takeaways from LocAgent
- Transformative graph-based indexing for effective code reasoning.
- Achieved up to 92.7% accuracy on SWE-Bench-Lite with Qwen2.5-32B.
- Significantly reduced localization costs by approximately 86% compared to proprietary models.
- Introduced Loc-Bench dataset, enhancing evaluation fairness.
- Essential tools like TraverseGraph and SearchEntity proved critical for accuracy.
- Improved GitHub issue resolution rates, demonstrating practical utility.
- Offers a scalable, cost-effective alternative to proprietary LLM solutions.
Conclusion
In summary, LocAgent presents a groundbreaking solution for code localization within software maintenance. By leveraging graph-based technology, it addresses the critical challenges of accurately identifying code modifications, improving efficiency, and reducing costs. Organizations can significantly benefit from adopting LocAgent, enhancing their software development processes while maintaining budgetary efficiency.
Next Steps
Explore how you can integrate artificial intelligence into your business processes. Identify areas where automation can add value, establish key performance indicators to assess AI impact, and consider starting with small projects to gradually expand your AI usage. For expert guidance on managing AI in business, contact us at hello@itinai.ru or follow us on our social media channels for further insights.



