Understanding Question Answering (QA) in Healthcare
Question answering (QA) is crucial in natural language processing, aimed at providing accurate answers to complex questions in various fields. In healthcare, medical QA faces unique challenges due to the intricate nature of medical information. It requires advanced reasoning skills to analyze patient data, medical conditions, and suggest evidence-based treatments through detailed, multi-step thinking.
Challenges in Traditional QA Systems
Traditional QA systems struggle to meet the specialized needs of the medical field, where in-depth decision-making is essential.
Innovative Approaches to Enhance Reasoning
Recent studies have explored various methods to improve reasoning capabilities in large language models (LLMs). Some effective techniques include:
- Chain-of-Thought Prompting: This technique improves reasoning by using structured sequences of thought.
- Monte Carlo Tree Search (MCTS): This method optimizes decision-making and exploration in complex scenarios.
- Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG): This technique allows LLMs to base their reasoning on the latest documents, enhancing their accuracy in medical contexts.
Introducing RARE: A New Solution
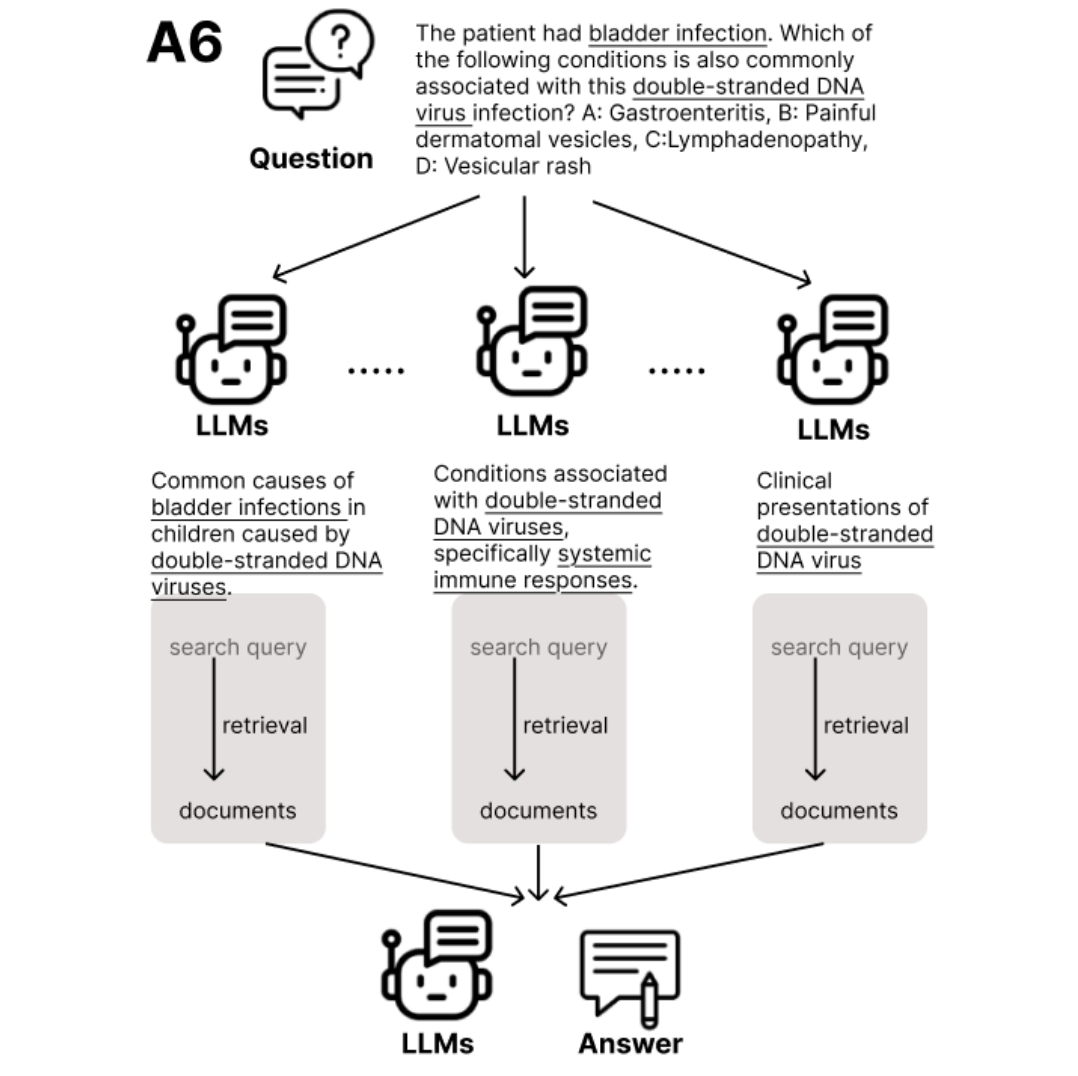
Researchers from multiple institutions have developed RARE (Retrieval-Augmented Reasoning Enhancement) to improve reasoning accuracy in complex tasks, especially in healthcare. This innovative solution includes:
- Query Generation: A mechanism for retrieving relevant information.
- Sub-Question Refinement: A strategy to refine inquiries for better insights.
RARE incorporates a Retrieval-Augmented Factuality Scorer (RAFC) to ensure high factual integrity and accuracy in reasoning.
How RARE Works
RARE employs a two-stage process:
- Candidate Generation: It uses a generator that fetches relevant external information to enhance reasoning paths.
- Factuality Evaluation: Instead of traditional models, it assesses reasoning paths to select the most factually supported answers.
Performance Highlights
RARE has shown outstanding performance in both medical and commonsense reasoning tasks, surpassing existing methods. For example, it achieved:
- 2.59% improvement on MedQA for the LLaMA3.2 3B model.
- 6.45% improvement in StrategyQA for the LLaMA3.1 8B model.
Future Potential and Limitations
RARE represents a significant advancement in reasoning capabilities but has limitations:
- It has only been tested on open-source models, not on larger proprietary models like GPT-4.
- It identifies a single reasoning path without optimizing for the best or quickest solution.
- It relies on MCTS without utilizing a trained reward model for dynamic guidance.
Get Involved and Explore AI Solutions
To stay competitive and transform your company with AI, consider integrating RARE to enhance reasoning in your operations.
- Identify Automation Opportunities: Find customer interaction points that can benefit from AI.
- Define KPIs: Ensure your AI initiatives have measurable impacts.
- Select an AI Solution: Choose customizable tools that meet your specific needs.
- Implement Gradually: Start with a pilot project, collect data, and expand wisely.
Connect for More Insights
For expert advice on AI KPI management, reach out to us at hello@itinai.com. For ongoing insights into leveraging AI, follow us on Telegram or @itinaicom.


























