Exploring the Potential of Large Language Models
Researchers are studying if large language models (LLMs) can do more than just language tasks. They want to see if LLMs can perform computations like traditional computers. The goal is to find out if an LLM can act like a universal Turing machine using only its internal functions.
Current Understanding and Challenges
LLMs are mainly used for tasks like text generation and translation. However, their full computational abilities are not yet clear. This research looks into whether LLMs can operate as universal computers without needing extra tools or memory upgrades.
Key Issues Addressed
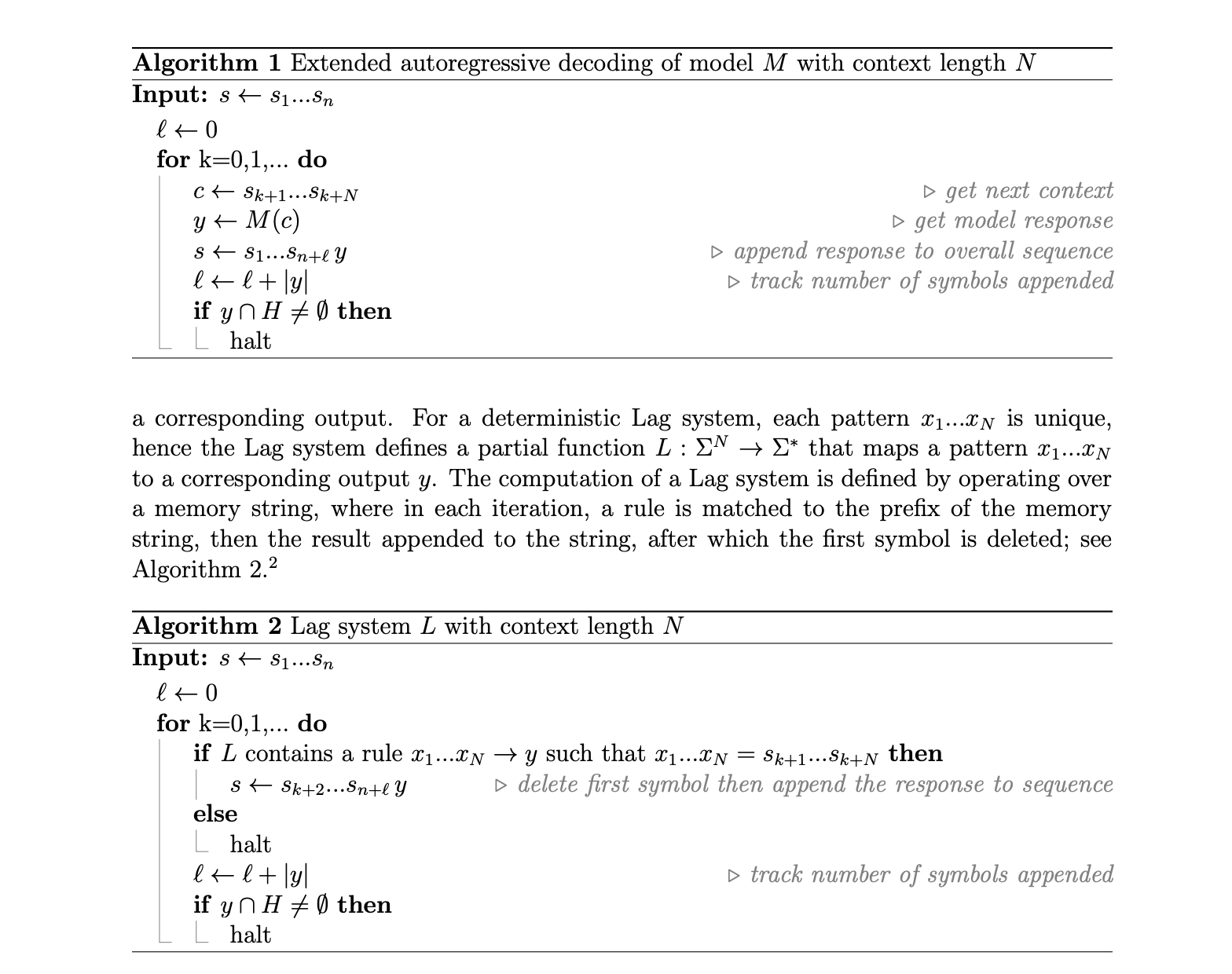
The main issue is the limits of language models, particularly transformer architectures. While they excel at recognizing patterns and generating text, there’s debate about whether they can perform any calculation a regular computer can. This study aims to clarify if a language model can independently achieve computational universality through a new decoding method that simulates infinite memory and processing.
Innovative Solutions Introduced
Researchers from Google DeepMind and the University of Alberta have proposed a method that enhances autoregressive decoding to handle long inputs. They created a system called the Lag system, which mimics memory operations found in classical Turing machines. This allows the model to process long sequences effectively, transforming it into a universal computational machine.
Research Findings
The team developed a prompt for the LLM gemini-1.5-pro-001 that employs 2,027 production rules under deterministic decoding. This method has been proven to simulate a universal Turing machine, showing that the language model can perform complex computations autonomously.
Key Discoveries
- LLMs can simulate any computational task that a traditional computer can under specific conditions.
- Generalized autoregressive decoding can turn an LLM into a universal computing entity when paired with a defined production rules system.
- Complex tasks can be completed within the model’s context window by managing memory during decoding.
- A single prompt can drive the model to execute advanced computations, making it a standalone general-purpose computer.
Conclusion and Future Implications
This research significantly enhances our understanding of LLMs’ capabilities. It shows that these models can simulate a universal Turing machine using only their internal functions, opening doors for more complex applications in various fields.
Stay Connected
Check out the research paper for more details. Follow us on Twitter, join our Telegram Channel, and be part of our LinkedIn Group. Don’t miss out on our newsletter and our 50k+ ML SubReddit community!
Upcoming Event
RetrieveX – The GenAI Data Retrieval Conference on Oct 17, 2023
Transform Your Business with AI
To stay competitive and leverage AI effectively, consider these steps:
- Identify Automation Opportunities: Find customer interaction points that can benefit from AI.
- Define KPIs: Ensure your AI initiatives have measurable impacts.
- Select an AI Solution: Choose tools that fit your needs.
- Implement Gradually: Start small, gather data, and expand wisely.
For AI KPI management advice, contact us at hello@itinai.com. For ongoing insights, follow us on Telegram or Twitter.
Enhance Your Sales and Customer Engagement with AI
Discover tailored solutions at itinai.com.



























