Researchers at Brown University Explore Zero-Shot Cross-Lingual Generalization of Preference Tuning in Detoxifying LLMs
Practical Solutions and Value
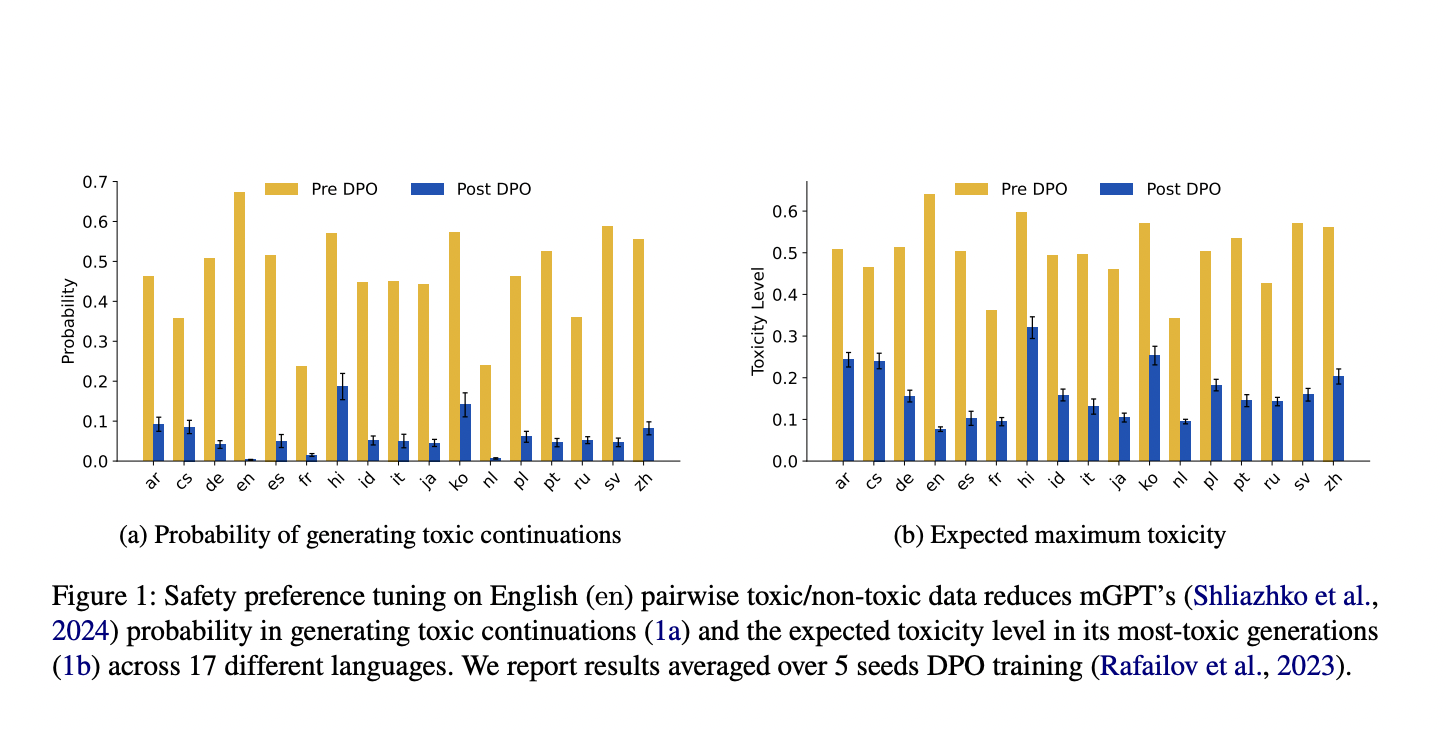
Large language models (LLMs) have raised concerns about safety in multilingual contexts. Researchers at Brown University have discovered a method to effectively reduce toxicity levels in LLM generations across 17 different languages. This approach offers a powerful solution for multilingual toxicity mitigation, addressing a critical challenge in LLM safety across diverse linguistic contexts.
Method Overview
The method involves localizing toxicity within the LLM using probes and performing causal interventions. By manipulating toxic neuron activations, the average toxicity level across 17 languages was significantly reduced. The study also reveals that toxic key vectors are multilingual, showing positive activation across many languages before the training and reduced activation across all languages after the detoxification process.
AI Solutions for Business
If you want to evolve your company with AI, stay competitive, and use AI for your advantage, consider leveraging the findings from Brown University’s research. Identify Automation Opportunities, Define KPIs, Select an AI Solution, and Implement Gradually. For AI KPI management advice, connect with us at hello@itinai.com. For continuous insights into leveraging AI, stay tuned on our Telegram channel or Twitter.



























