Introduction to MLE-bench
Machine Learning (ML) models can perform various coding tasks, but there is a need to better evaluate their capabilities in ML engineering. Current benchmarks often focus on basic coding skills, neglecting complex tasks like data preparation and model debugging.
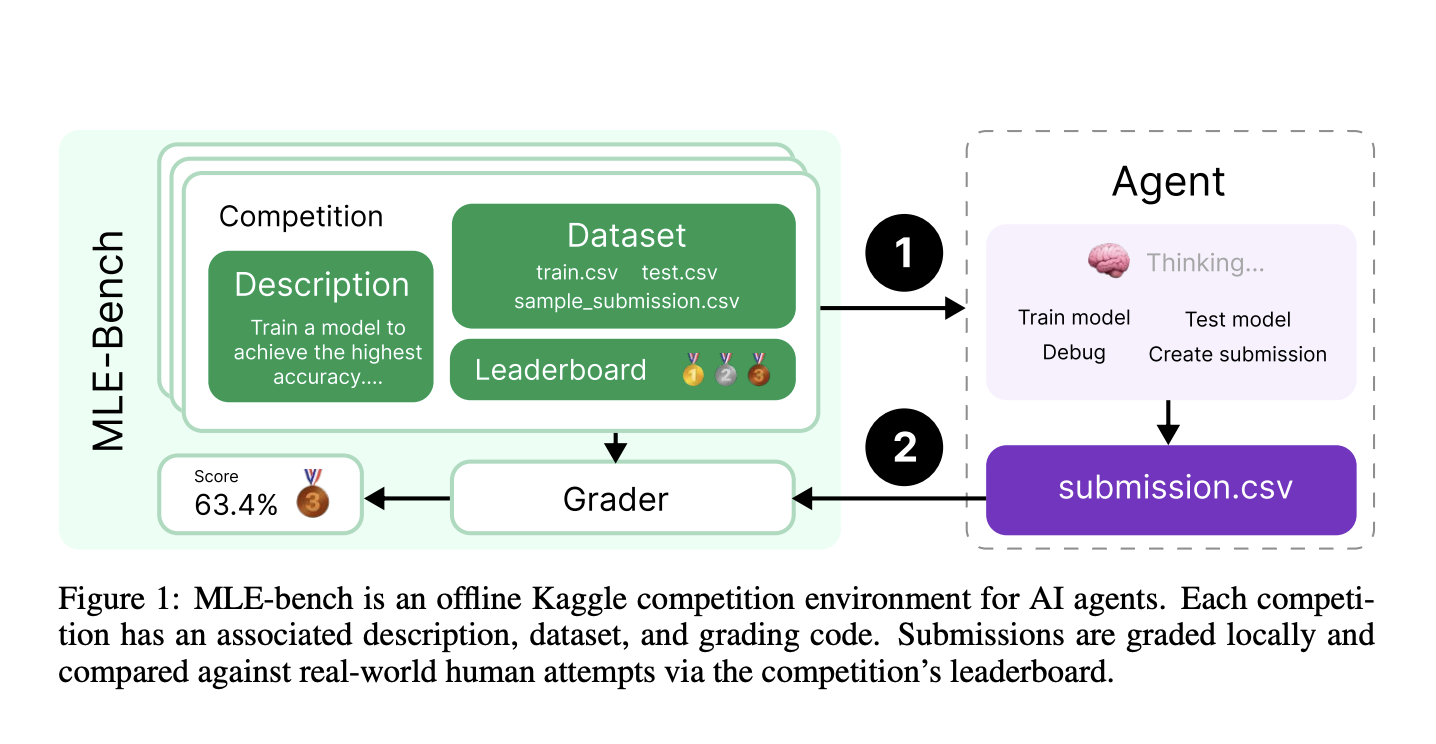
What is MLE-bench?
To fill this gap, OpenAI researchers created MLE-bench. This new benchmark tests AI agents across a wide range of real-world ML engineering challenges, using 75 curated competitions from Kaggle. These challenges include areas like natural language processing and computer vision, evaluating crucial skills such as:
- Training models
- Data preprocessing
- Running experiments
- Submitting results
MLE-bench includes human performance metrics from Kaggle to fairly compare AI agents with expert participants.
Structure of MLE-bench
MLE-bench is designed to rigorously evaluate ML engineering skills. Each competition includes:
- A problem description
- A dataset
- Local evaluation tools
- Grading code
The datasets are split into training and testing sets with no overlap, ensuring accurate assessments. AI agents are graded on performance relative to human attempts, earning medals based on their results. Key evaluation metrics include AUROC and mean squared error, allowing fair comparisons with Kaggle participants.
Performance Insights
The evaluation showed that OpenAI’s o1-preview model performed well, with medals achieved in 16.9% of competitions. Results improved significantly with repeated attempts, illustrating that while AI agents can follow known methods, they struggle to correct initial mistakes without several tries. Additionally, having more resources, like increased computing time, led to better performance.
Conclusion and Future Directions
MLE-bench is a major advancement in assessing AI agents’ abilities in ML engineering tasks. It focuses on practical skills that are essential for real-world applications. OpenAI aims to open-source MLE-bench to promote collaboration and encourage researchers to enhance the benchmark and explore new techniques. This initiative will help identify areas for AI improvement and contribute to safer, more reliable AI systems.
Getting Started with MLE-bench
To use MLE-bench, some data is stored using Git-LFS. After installing LFS, run:
- git lfs fetch –all
- git lfs pull
You can install MLE-bench with:
pip install -e .
Connect with Us
For continuous updates and insights, follow us on our social channels and subscribe to our newsletter. If you’re looking to integrate AI into your business, reach out at hello@itinai.com.
Transform Your Business with AI
Discover how AI can optimize your workflows:
- Identify automation opportunities
- Define measurable KPIs
- Choose suitable AI solutions
- Implement AI gradually with pilot projects
Learn more at itinai.com.



