Enhancing Large Language Models (LLMs) for Business Efficiency
Understanding the Challenge
Large Language Models (LLMs) have made remarkable strides in structured reasoning, enabling them to solve complex mathematical problems, derive logical conclusions, and perform multistep planning. However, these advancements come with a significant drawback: the high computational resources required for processing lengthy reasoning sequences. This inefficiency can lead to increased costs and slower performance, which are critical concerns for businesses looking to leverage AI technology.
Current Solutions and Limitations
Efforts to enhance LLM efficiency have focused on compressing reasoning traces to minimize redundancy. While some methods utilize continuous latent representations or iterative reductions, they often involve complex training processes that do not match the performance of models using full-text reasoning. This highlights the need for a more effective solution that balances computational efficiency with reasoning capabilities.
Innovative Approaches: The Latent Token Method
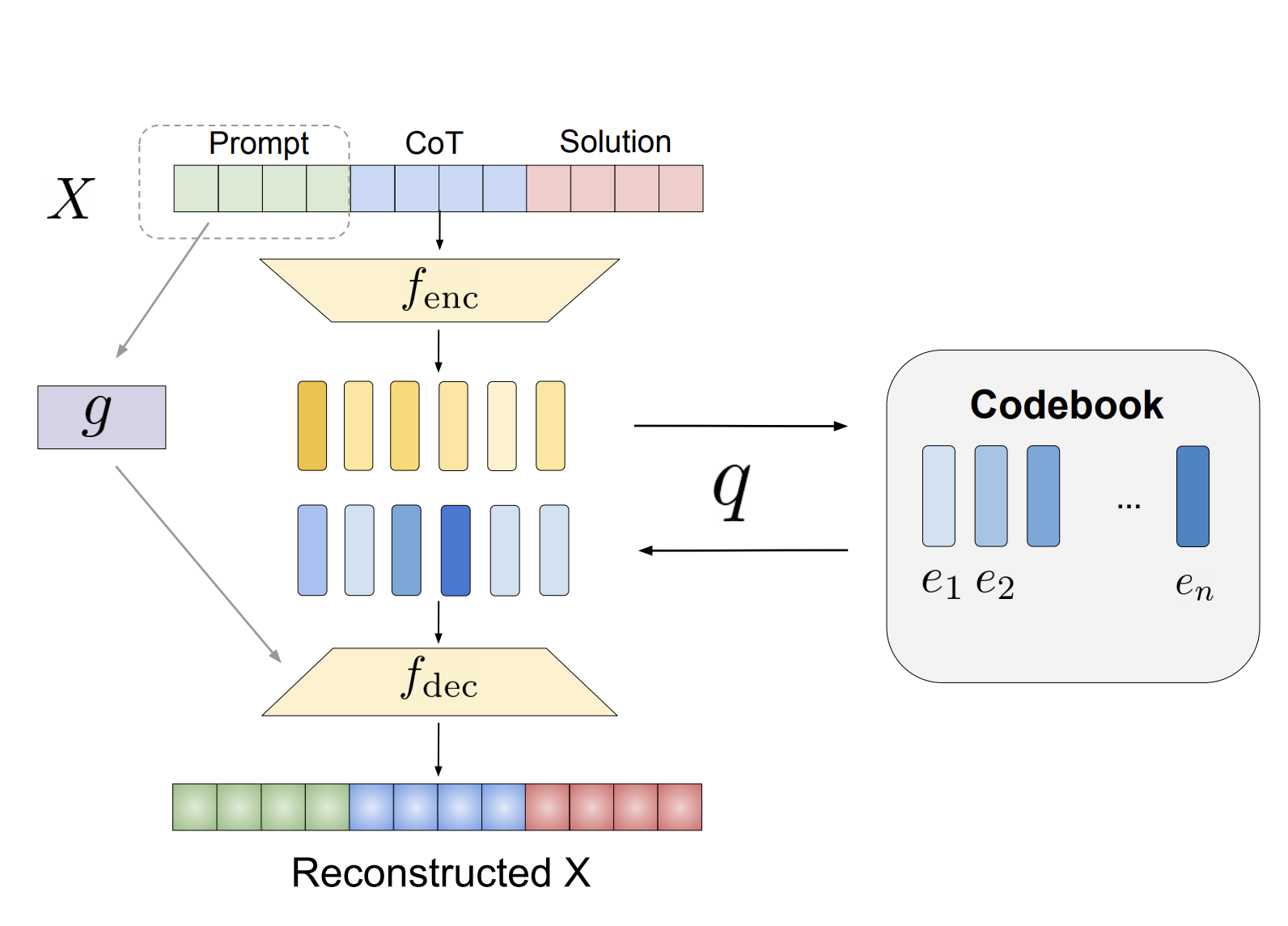
A groundbreaking technique developed by researchers from Meta AI and UC Berkeley introduces the use of discrete latent tokens to improve LLM reasoning. This method employs a vector-quantized variational autoencoder (VQ-VAE) to convert parts of the reasoning process into compact representations. By replacing early reasoning steps with these latent abstractions while keeping later steps in text form, the model maintains interpretability and reduces the overall token length of reasoning sequences.
Training Strategy and Adaptability
The researchers implemented a training strategy that incorporates latent tokens into LLM reasoning. By randomly replacing a portion of reasoning steps with their latent counterparts, the model learns to interpret both abstracted and explicit reasoning structures. This adaptability across various problem types enhances the model’s generalization ability while reducing computational demands.
Performance Improvements and Case Studies
The proposed method has shown significant performance gains across multiple benchmarks. For instance, in mathematical reasoning tasks, it achieved a 4.2% improvement over previous best-performing methods on the Math dataset. Similarly, it recorded a 4.1% gain on the GSM8K benchmark and a remarkable 13.3% improvement on the Fresh-Gaokao-Math-2023 dataset. Additionally, the reduction in reasoning trace length by an average of 17% resulted in faster inference times and lower memory usage. Evaluations on logical reasoning datasets such as ProntoQA and ProsQA further validated the approach, with accuracy improvements of 1.2% and 18.7%, respectively.
Practical Business Solutions
- Automation Opportunities: Identify processes within your organization that can be automated using AI, particularly in customer interactions where AI can add significant value.
- Key Performance Indicators (KPIs): Establish important KPIs to measure the impact of your AI investments on business outcomes.
- Tool Selection: Choose AI tools that align with your business needs and allow for customization to meet specific objectives.
- Start Small: Initiate AI projects on a smaller scale, gather data on their effectiveness, and gradually expand your AI applications based on proven success.
Conclusion
The introduction of latent tokens represents a significant advancement in optimizing LLM reasoning without sacrificing accuracy. By minimizing reliance on full-text reasoning sequences and leveraging discrete latent representations, businesses can achieve greater efficiency while maintaining high reasoning capabilities. As LLMs continue to evolve, such innovative methods will pave the way for more resource-efficient AI systems, ultimately transforming how organizations operate and make decisions.




























