Challenges in Robotic Manipulation
Robotic manipulation tasks present significant challenges for reinforcement learning. This is mainly due to:
- Sparse rewards that limit feedback
- High-dimensional action-state spaces
- Difficulty in designing effective reward functions
Conventional reinforcement learning struggles with exploration efficiency, leading to suboptimal learning, especially in tasks requiring multi-stage reasoning.
Previous Solutions
Earlier research explored several methods to address these challenges:
- Model-based reinforcement learning: Improves sample efficiency using predictive models but requires extensive exploration.
- Demonstration-based learning: Utilizes expert demonstrations but faces scalability issues due to the need for large datasets.
- Inverse reinforcement learning: Learns reward functions from demonstrations but struggles with generalization and complexity.
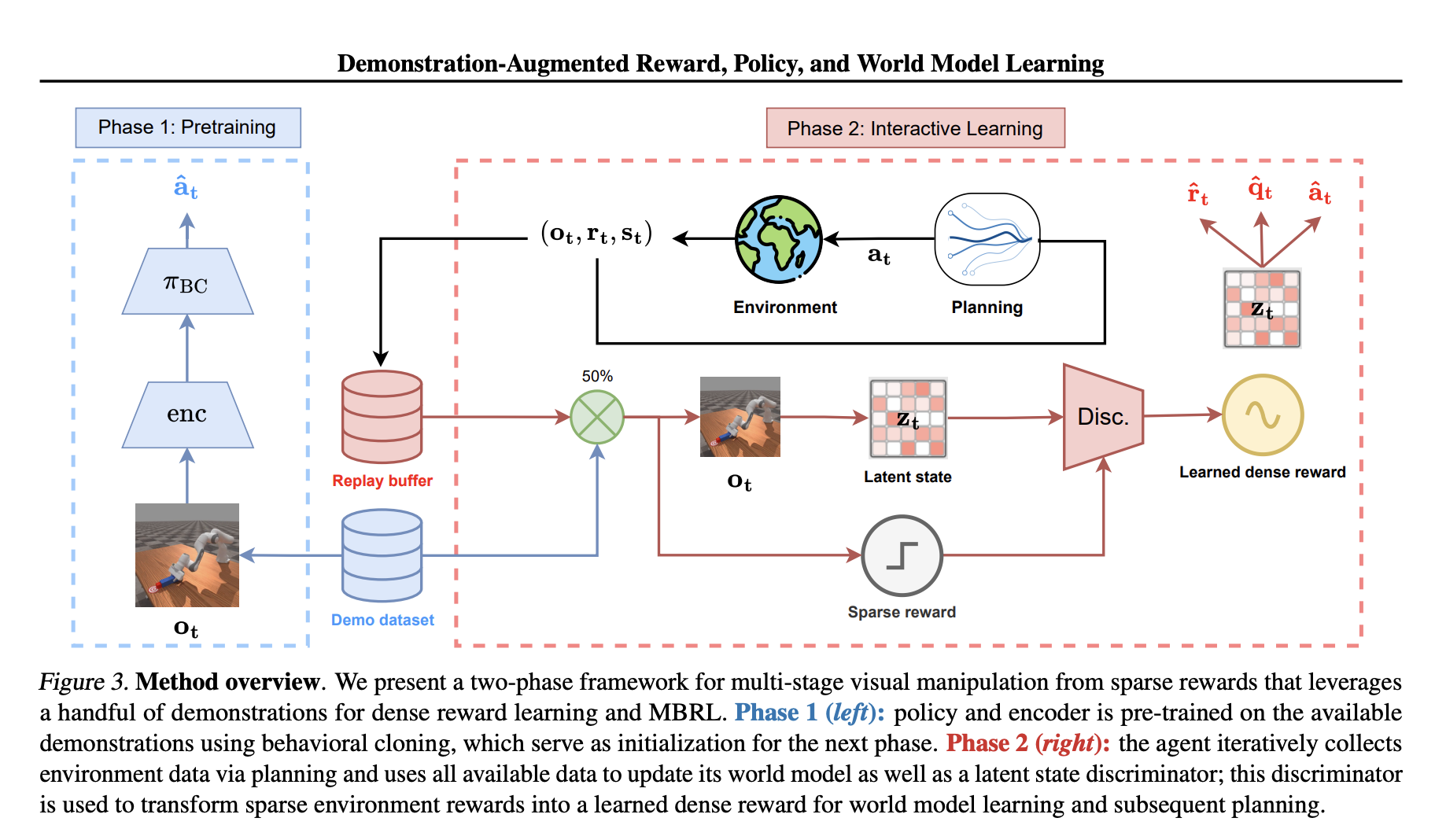
Introducing DEMO3
To overcome these limitations, a new framework called Demonstration-Augmented Reward, Policy, and World Model Learning (DEMO3) has been developed. This innovative approach includes:
- Transforming sparse rewards into continuous, structured rewards for reliable feedback.
- A bi-phasic training schedule combining behavioral cloning and interactive reinforcement learning.
- Online world model learning for dynamic penalty adaptation during training.
Key Features of DEMO3
DEMO3 leverages:
- Stage-specific discriminators to forecast progress toward subgoals, enhancing learning signals.
- A systematic two-phase training process: pre-training with behavioral cloning followed by continuous reinforcement learning.
- An efficient shift from imitation to policy improvement.
This framework has been tested on various complex robotic tasks and shows substantial improvements in efficiency and robustness.
Performance Benefits
Compared to existing algorithms, DEMO3 demonstrates:
- Average improvements of 40% in data efficiency, with up to 70% for challenging tasks.
- High success rates with minimal demonstrations.
- Effective handling of multi-stage tasks like peg insertion and cube stacking.
- Competitive computational costs, averaging 5.19 hours for 100,000 interaction steps.
Conclusion
DEMO3 marks a significant advancement in reinforcement learning for robotic control. By utilizing structured reward learning, policy optimization, and model-based decision-making, it achieves superior performance and efficiency. Future research can focus on enhancing demonstration sampling and adaptive reward strategies to further improve data efficiency.
Get Involved
Discover how artificial intelligence can transform business operations. Identify processes for automation and key performance indicators to measure AI impact. Start with small projects to evaluate effectiveness, then scale your AI initiatives.
For guidance on managing AI in your business, contact us at hello@itinai.ru or visit us on:
“`


























