Challenges of Implementing AI in Clinical Disease Management
Large language models (LLMs) face significant challenges in clinical disease management. While they excel in diagnostic reasoning, their effectiveness in ongoing disease management, medication prescriptions, and multi-visit patient care remains untested. Key challenges include:
- Limited understanding of patient context over multiple visits.
- Inconsistent adherence to clinical guidelines.
- Complexities in medication reasoning.
- The need for real-time, high-quality patient interactions.
Addressing these issues is crucial for developing AI systems that can support healthcare professionals in delivering accurate and personalized care.
Current Limitations of AI in Healthcare
Previous AI models primarily focused on diagnostics, relying on structured data for differential diagnoses. However, these models struggle in real-world settings:
- Many fail to track patient history effectively across visits, leading to inconsistent care recommendations.
- Some models do not align well with clinical guidelines, reducing the reliability of management plans.
- Medication reasoning often results in inconsistencies regarding drug choices, dosages, and interactions.
- The need for rapid decision-making in clinical environments creates computational bottlenecks.
Innovative Solutions from Google Researchers
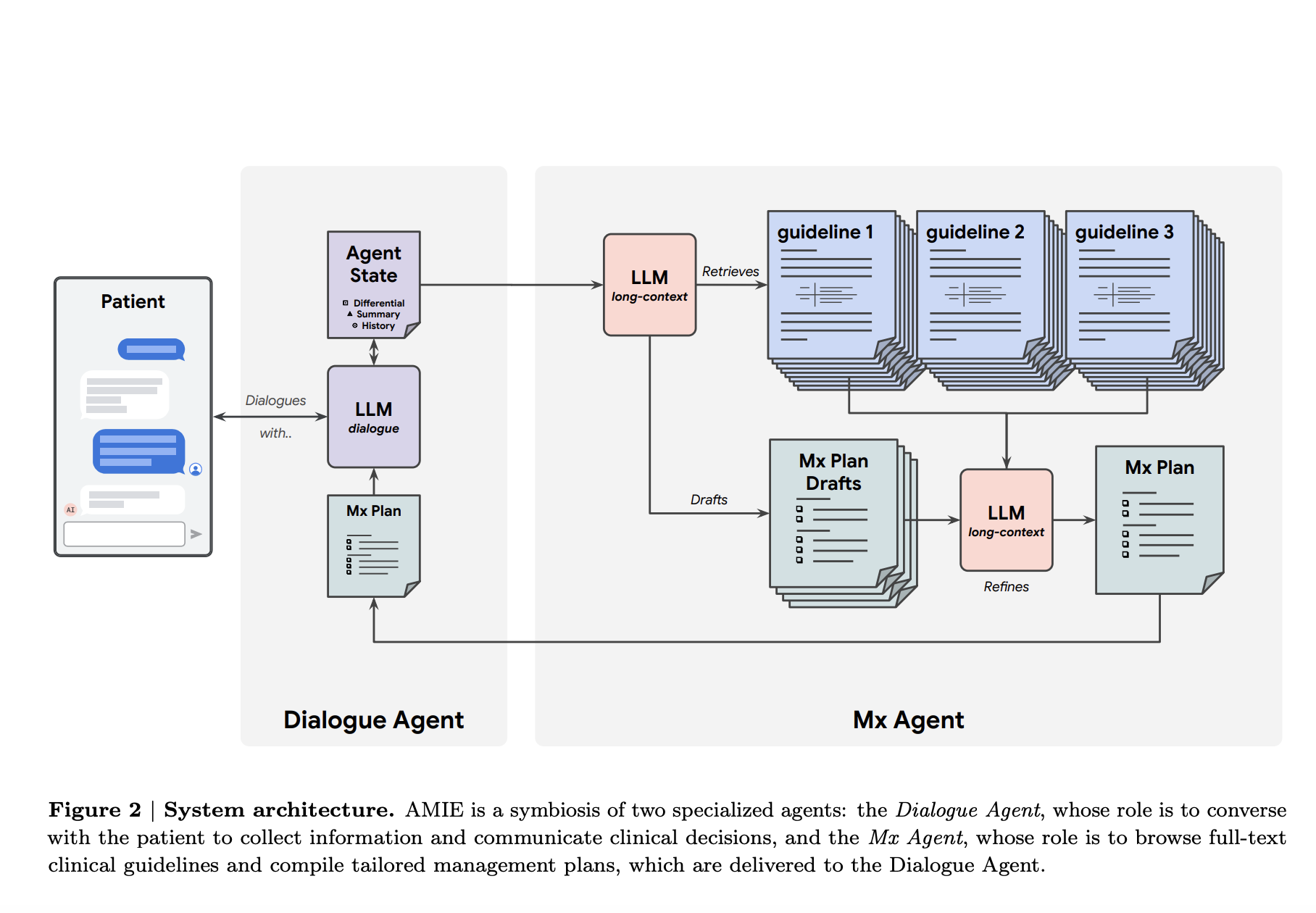
Google researchers have developed a groundbreaking LLM-based system for managing clinical disease and multi-visit patient interactions. This system includes:
- A Dialogue Agent that facilitates natural conversations and tracks patient history.
- A Management Reasoning (Mx) Agent that utilizes clinical guidelines and patient data to create structured treatment plans.
- Gemini’s extended-context capabilities to ensure alignment with current guidelines and drug formularies.
This innovative approach allows for dynamic management of patient interactions, evolving recommendations based on patient progress.
Performance and Assessment
The AI system’s performance was evaluated through a virtual Objective Structured Clinical Examination (OSCE) against 21 primary care physicians across 100 multi-visit cases. Key findings include:
- The AI system matched or outperformed physicians in disease management reasoning.
- It demonstrated superior accuracy in treatment and medication reasoning.
- The AI provided structured management plans with better adherence to clinical guidelines.
Additionally, the RxQA benchmark was introduced to assess medication reasoning, demonstrating improved performance over human clinicians in complex drug-related tasks.
Implications for Healthcare Delivery
This AI system represents a significant advancement in disease management, moving beyond simple diagnostics to comprehensive patient care. Its capabilities include:
- Deep contextual reasoning and coordination among multiple agents.
- Real-time retrieval of clinical guidelines to support decision-making.
- Accurate treatment recommendations and adherence to protocols.
While further research is required for real-world applications, this development marks a crucial step in enhancing primary care and improving healthcare delivery through AI automation.
Next Steps for Businesses
To harness the potential of AI in your organization, consider the following:
- Explore how AI can transform your workflows and identify automation opportunities.
- Determine key performance indicators (KPIs) to assess the impact of your AI investments.
- Select customizable tools that align with your objectives.
- Start with small projects, evaluate their effectiveness, and gradually expand AI applications.
For guidance on managing AI in your business, contact us at hello@itinai.ru or connect with us on Telegram, X, and LinkedIn.




























