Introduction to Sentiment Analysis
In this tutorial, we will explore how to perform sentiment analysis on text data using IBM’s open-source Granite 3B model integrated with Hugging Face Transformers. Sentiment analysis is a crucial natural language processing (NLP) technique that helps businesses understand customer emotions through feedback, enabling them to improve their products and services.
Installing Necessary Libraries
First, we need to install the essential libraries: transformers, torch, and accelerate. These libraries allow us to load and run powerful NLP models seamlessly.
!pip install transformers torch accelerate
Importing Required Libraries
Next, we will import the required Python libraries:
import torch from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM, AutoTokenizer, pipeline import pandas as pd import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
These libraries will assist us in tensor operations, loading pre-trained NLP models, managing data, and visualizing our analysis results.
Loading the IBM Granite Model
We will load IBM’s Granite 3B model using Hugging Face:
model_id = "ibm-granite/granite-3.0-3b-a800m-instruct"
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(model_id)
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(
model_id,
device_map='auto',
torch_dtype=torch.bfloat16,
trust_remote_code=True
)
generator = pipeline("text-generation", model=model, tokenizer=tokenizer)
This model is optimized for tasks such as sentiment classification, even with limited computational resources.
Defining the Sentiment Classification Function
We will create a function that classifies the sentiment of a review:
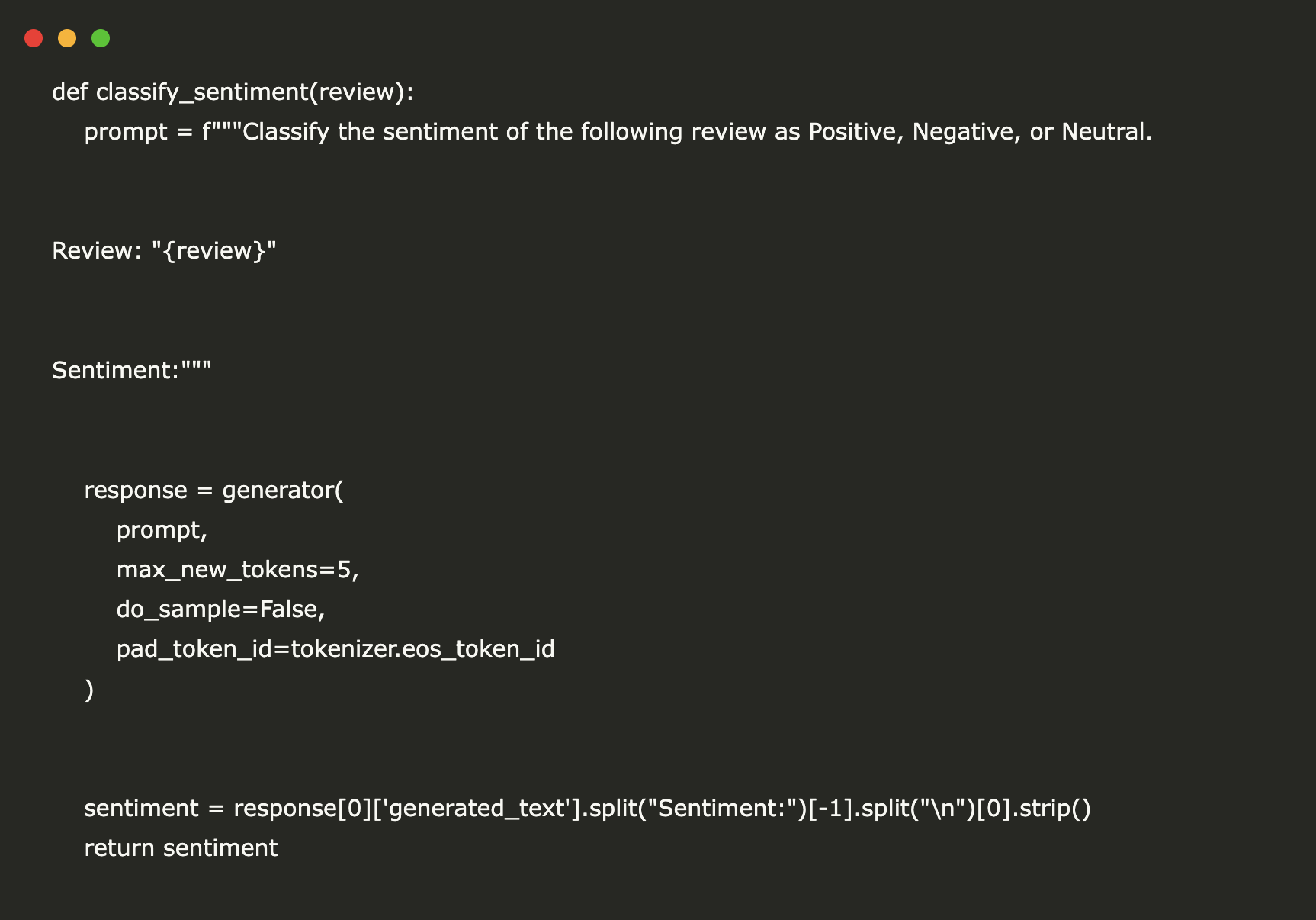
def classify_sentiment(review):
prompt = f"""Classify the sentiment of the following review as Positive, Negative, or Neutral.
Review: "{review}"
Sentiment:"""
response = generator(
prompt,
max_new_tokens=5,
do_sample=False,
pad_token_id=tokenizer.eos_token_id
)
sentiment = response[0]['generated_text'].split("Sentiment:")[-1].split("n")[0].strip()
return sentiment
Creating a DataFrame of Reviews
We will create a DataFrame to hold example reviews for sentiment classification:
reviews = [
"I absolutely loved the service! Definitely coming back.",
"The item arrived damaged, very disappointed.",
"Average product. Nothing too exciting.",
"Superb experience, exceeded all expectations!",
"Not worth the money, poor quality."
]
reviews_df = pd.DataFrame(reviews, columns=['review'])
Classifying Sentiments
Now, we will apply the sentiment classification function to each review:
reviews_df['sentiment'] = reviews_df['review'].apply(classify_sentiment) print(reviews_df)
Visualizing Sentiment Distribution
Finally, we will visualize the sentiment distribution using a pie chart:
sentiment_counts = reviews_df['sentiment'].value_counts()
plt.figure(figsize=(8, 6))
sentiment_counts.plot.pie(autopct='%1.1f%%', explode=[0.05]*len(sentiment_counts), colors=['#66bb6a', '#ff7043', '#42a5f5'])
plt.ylabel('')
plt.title('Sentiment Distribution of Reviews')
plt.show()
Conclusion
We have successfully implemented a sentiment analysis pipeline using IBM’s Granite 3B model. This method allows businesses to classify customer sentiments quickly and visualize insights effectively. By leveraging these skills, you can apply the same approach to analyze other datasets or explore various NLP tasks.
Further Reading and Resources
Explore how AI technology can transform your business processes. Identify key performance indicators (KPIs) to assess your AI investments, select suitable tools for your needs, and start with small projects to gather data on effectiveness.
For guidance on managing AI in business, please contact us at hello@itinai.ru. Follow us on Telegram, Twitter, and LinkedIn.


























