Addressing Language Imbalance in AI
Many existing large language models (LLMs) focus primarily on languages with ample training resources, such as English, French, and German. This leaves widely spoken but underrepresented languages like Hindi, Bengali, and Urdu with limited support. This gap restricts access to high-quality AI language tools for billions of people worldwide. To tackle this issue, innovative training methods for multilingual LLMs are necessary to ensure consistent performance across languages with varying levels of resources.
The Challenge of Multilingual NLP
A significant hurdle in multilingual natural language processing (NLP) is the uneven distribution of linguistic resources. High-resource languages benefit from extensive training data, while languages in developing regions often lack sufficient datasets. This disparity results in multilingual models performing better with well-documented languages while struggling with those that are underrepresented. Solutions must aim to broaden language coverage without sacrificing model efficiency.
Current Initiatives in Multilingual LLMs
Several multilingual LLMs, such as Bloom, GLM-4, and Qwen2.5, have attempted to address these challenges. However, their performance largely depends on the availability of training data, often excelling in languages like English, Chinese, and Spanish while underperforming in languages with less data, such as Swahili, Javanese, or Burmese. Many of these models also rely on traditional pretraining methods, which do not effectively accommodate language diversity without increasing computational demands.
Introducing Babel: A Multilingual Solution
Researchers from DAMO Academy at Alibaba Group have developed Babel, a multilingual LLM that supports over 90% of global speakers by covering the top 25 most spoken languages. Babel utilizes a unique layer extension technique that enhances model capacity without sacrificing performance. Two variants have been introduced: Babel-9B, optimized for efficiency, and Babel-83B, which sets a new standard in multilingual NLP. Babel incorporates languages that are often overlooked, such as Bengali, Urdu, Swahili, and Javanese, focusing on high-quality training data through a rigorous curation process.
Innovative Architecture and Training Methods
Babel’s architecture differs from traditional multilingual LLMs by employing a structured layer extension approach rather than continuous pretraining, thus conserving computational resources. The model’s parameter count is increased through controlled expansion, enabling Babel-9B to balance speed and multilingual comprehension effectively. Babel-83B extends capabilities to match commercial models. The training process includes extensive data-cleaning techniques using an LLM-based quality classifier, with data sourced from diverse origins like Wikipedia and structured multilingual corpora.
Performance and Evaluation
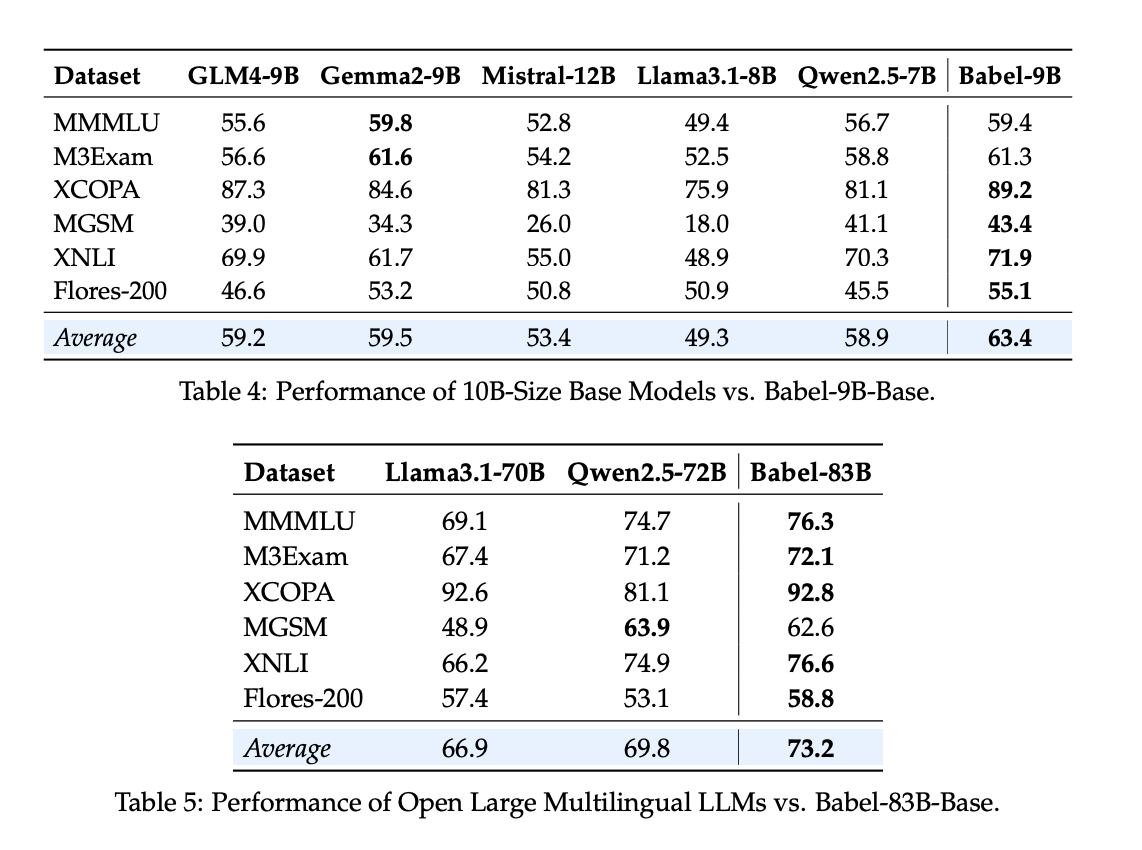
Evaluation metrics show Babel’s superiority over existing multilingual LLMs. Babel-9B achieved an average score of 63.4 across multiple benchmarks, outperforming competitors such as GLM4-9B and Gemma2-9B. Babel-83B set a new benchmark with an average score of 73.2, excelling particularly in low-resource languages with improvements of 5-10% over previous models. The supervised fine-tuning (SFT) models have shown performance comparable to commercial AI models like GPT-4o.
Key Takeaways
- Babel supports 25 widely spoken languages, reaching over 90% of global speakers.
- It employs a structured layer extension technique to enhance scalability without excessive computational demands.
- The training corpus includes high-quality data from various sources, ensuring linguistic accuracy.
- Babel-9B and Babel-83B demonstrate state-of-the-art performance across reasoning, translation, and multilingual understanding tasks.
- Significant accuracy improvements for underrepresented languages have been achieved.
Next Steps
To leverage AI effectively in your business, consider the following:
- Explore how AI technology can transform your work processes.
- Identify areas where AI can add value, particularly in customer interactions.
- Establish key performance indicators (KPIs) to measure the impact of your AI investments.
- Select customizable tools that align with your business objectives.
- Start with small projects, gather data on their effectiveness, and gradually expand your AI initiatives.
Contact Us
If you need guidance on managing AI in business, contact us at hello@itinai.ru. Follow us on Telegram, X, and LinkedIn.


























