What is an Agent?
An agent is a system powered by a Large Language Model (LLM) that can manage its own workflow. Unlike traditional chatbots, agents can:
- Choose actions based on context.
- Utilize external tools like web searches, databases, or APIs.
- Iterate through steps for improved problem-solving.
This adaptability makes agents ideal for complex tasks such as research, data analysis, or multi-step workflows.
Key Components of Agents
Understanding the components of agents is essential for effective implementation:
Agent (LLM Core)
The core of every agent is the LLM, which:
- Interprets user inputs to understand their intent.
- Decides next steps based on prompts and available tools.
Memory
Memory allows agents to maintain context and learn:
- Short-term memory: Tracks current interactions.
- Long-term memory: Stores past interactions for personalized responses.
Tools
Tools enhance an agent’s capabilities beyond text generation, allowing it to:
- Perform web searches for the latest information.
- Use calculators for complex math.
- Access APIs for services like weather updates or stock data.
What is LangGraph?
LangGraph is a Python library that helps create stateful, multi-step AI workflows. It connects the agent’s components for efficient interaction.
What Does LangGraph Offer?
LangGraph simplifies building intelligent agents by providing tools to:
- Create decision-making loops for guiding workflows.
- Connect LLMs to external tools for added functionality.
- Manage shared memory for smooth transitions between steps.
Key Concepts
LangGraph is structured around three main concepts:
- Nodes: Basic units of work, like calling an LLM or performing a web search.
- Edges: Connections that define the operation sequence.
- State: Shared data that tracks progress and context.
Let’s Build a Simple Agent
Step 1: Setup
First, install the necessary packages:
pip install langgraph langchain-community langchain-core langchain-groqNext, obtain free API keys for the tools:
- Groq for LLM access.
- Tavily for web search functionality.
Set your environment variables to store the API keys securely.
Step 2: Basic Chatbot
We will create a simple chatbot using Groq’s LLM.
1. Import Dependencies
from langgraph.graph import StateGraph, START, END, MessagesState2. Initialize LLM
llm = ChatGroq(temperature=0, model="Llama-3.3-70b-Specdec")3. Define AgentState
class AgentState(TypedDict): messages: Annotated[list[AnyMessage], operator.add]4. Define Workflow and Create Agent
# Build graph
graph = StateGraph(AgentState)
graph.add_node("llm", call_llm)
graph.add_edge(START, "llm")
graph.add_edge("llm", END)
agent = graph.compile()Step 3: Add Web Search Tool
Enhance the agent by integrating a web search tool.
1. Define the Tool
from langchain_community.tools.tavily_search import TavilySearchResults2. Binding the Tool with LLM
model = llm.bind_tools(tools)3. Enhanced Workflow
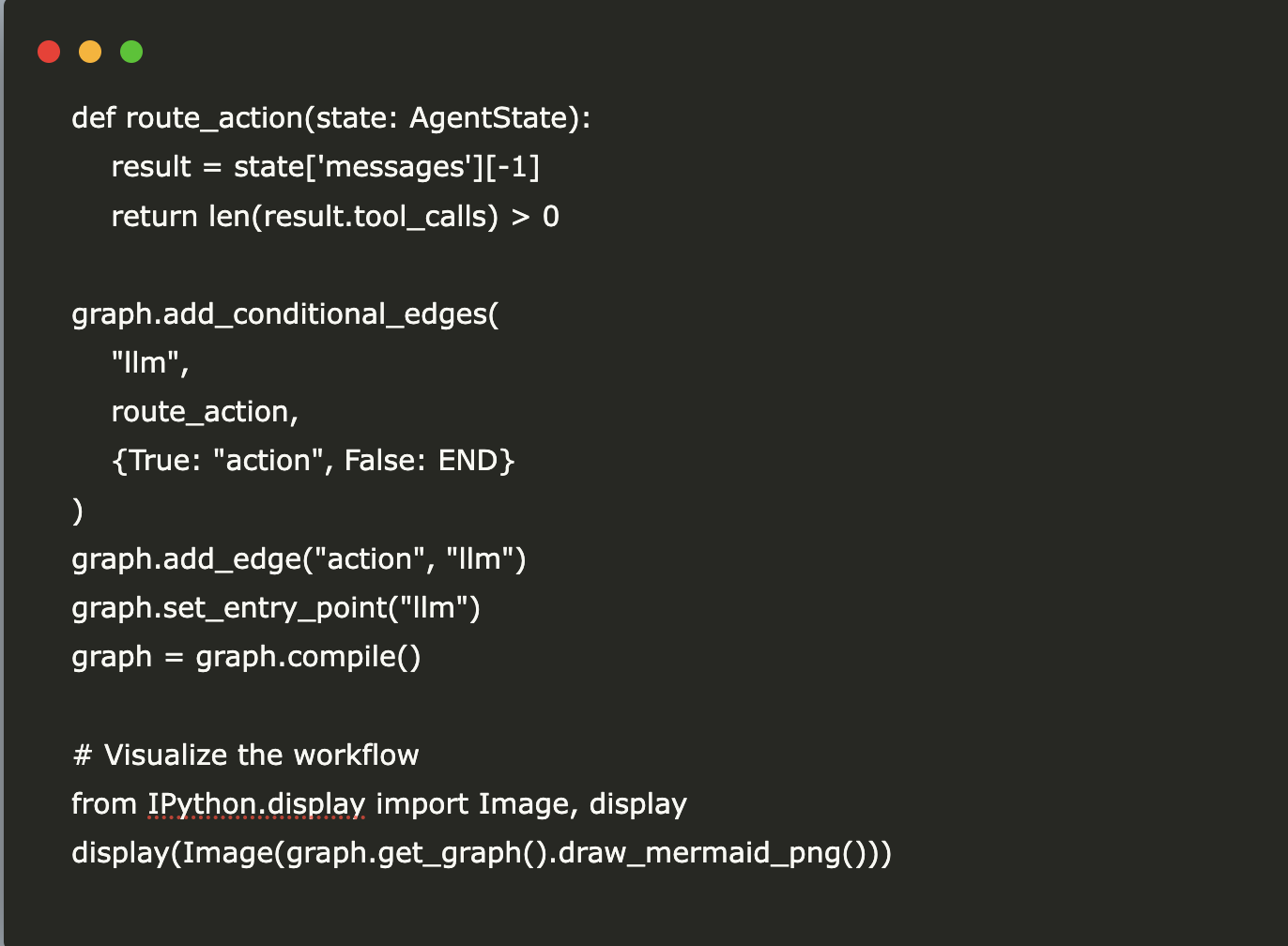
def take_action(state: AgentState): ...4. Adding the Conditional Edge
def route_action(state: AgentState): ...Next Steps
Now that you have a functional agent, consider expanding its capabilities:
- Add More Tools: Include calculators or database connectors.
- Implement Memory: Store session-specific data for follow-up questions.
- Create Multi-Agent Systems: Use multiple specialized agents for complex tasks.
Congratulations! You’ve built an AI agent capable of:
- Making dynamic decisions.
- Using external tools for real-time information.
- Refining responses through iterative processing.
Explore LangGraph to create your own intelligent agents tailored to specific tasks!
Discover AI Solutions
Transform your business with AI by:
- Identifying Automation Opportunities: Find key interaction points for AI benefits.
- Defining KPIs: Ensure measurable impacts from AI initiatives.
- Selecting AI Solutions: Choose tools that meet your needs.
- Implementing Gradually: Start small, gather data, and expand AI usage.
For AI KPI management advice, connect with us at hello@itinai.com. Stay updated on AI insights through our Telegram or follow us on @itinaicom.

























