Understanding Haystack Agents
Haystack Agents are a powerful feature of the Haystack NLP framework designed to enhance Natural Language Processing (NLP) tasks. They allow for:
- Complex reasoning: Work through multiple steps to arrive at an answer.
- Tool integration: Use external tools or APIs to increase functionality.
- Advanced workflows: Go beyond simple question answering.
Why Use Haystack Agents?
Haystack Agents stand out for specialized tasks, making them more efficient than general frameworks like LangChain. Key benefits include:
- Document retrieval efficiency: Quickly search through large datasets.
- Custom tool integration: Easily add APIs for calculations or database interactions.
- Complex query handling: Effectively solve logical challenges.
- Open-source flexibility: Integrate smoothly with popular machine learning libraries like Elasticsearch and Hugging Face models.
How Haystack Agents Work
Haystack Agents leverage a modular architecture where:
- Tools: Perform specific tasks like searching documents or calculating results.
- Dynamic decision-making: Agents choose which tools to use and how to combine their outputs.
- Retrievers: Facilitate efficient document searches within vast datasets.
Practical Example: Building a QA Agent
In this guide, we’ll create a QA Agent that:
- Answers questions from a document store.
- Performs calculations using a calculator tool.
- Combines results as needed.
Step 1: Prepare Your Environment
Set up your environment with these steps:
- Install Python 3.8 or higher.
- Install Haystack: pip install farm-haystack[all]
- Launch Elasticsearch for document storage: docker run -d -p 9200:9200 -e “discovery.type=single-node” docker.elastic.co/elasticsearch/elasticsearch:7.17.1
Step 2: Create the Document Store and Retriever
Set up your document store for storing and retrieving data:
from haystack.utils import launch_es from haystack.nodes import EmbeddingRetriever from haystack.pipelines import DocumentSearchPipeline from haystack.document_stores import ElasticsearchDocumentStore launch_es() document_store = ElasticsearchDocumentStore() document_store.write_documents(docs) retriever = EmbeddingRetriever(document_store=document_store, embedding_model="sentence-transformers/all-MiniLM-L6-v2", use_gpu=True) document_store.update_embeddings(retriever)
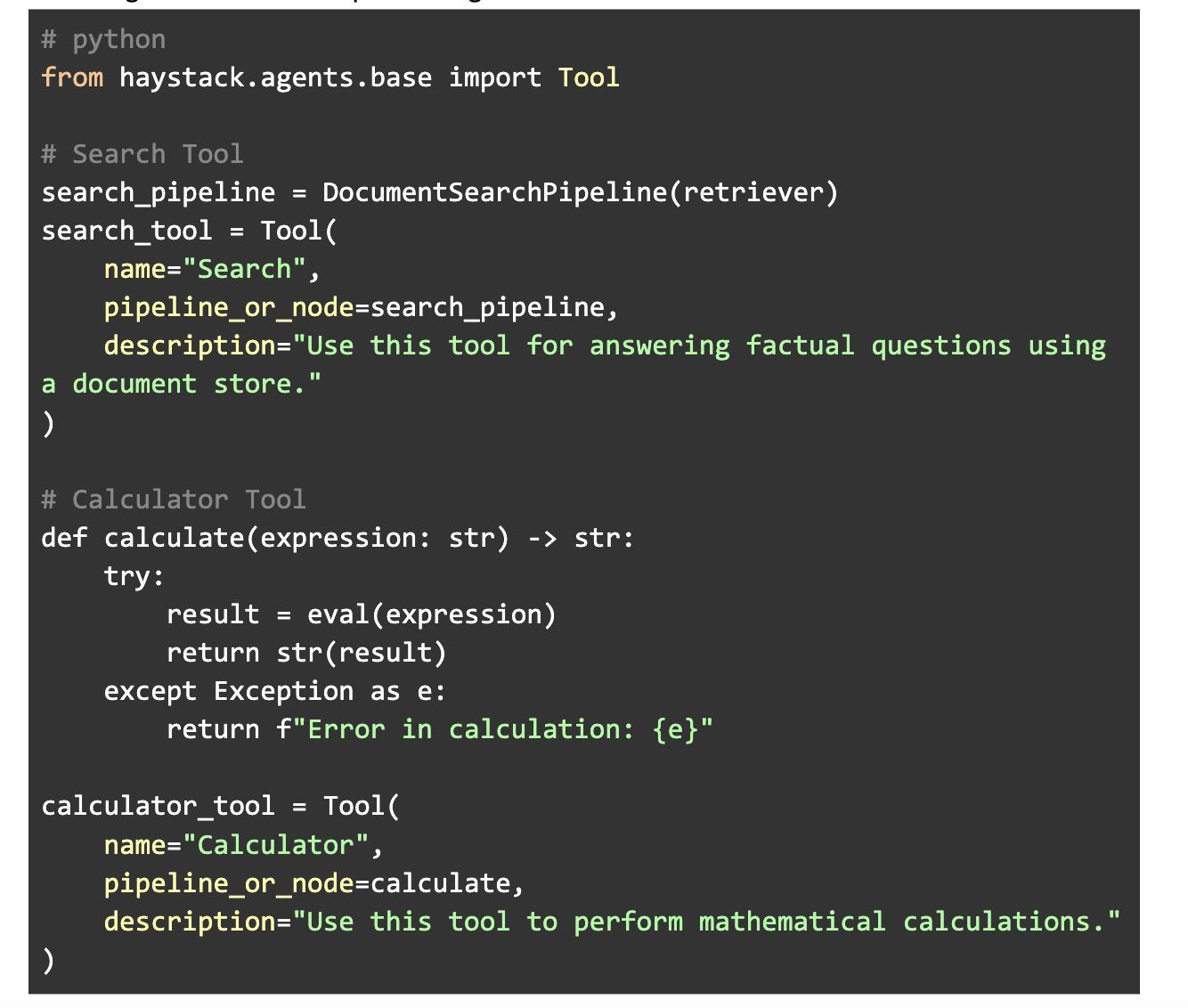
Step 3: Define the Tools
Tools are essential for your agent’s functionality:
from haystack.agents.base import Tool
search_tool = Tool(name="Search", pipeline_or_node=DocumentSearchPipeline(retriever),
description="Answers factual questions using a document store.")
calculator_tool = Tool(name="Calculator", pipeline_or_node=calculate,
description="Performs mathematical calculations.")
Step 4: Initialize the Agent
Configure your agent with the necessary tools:
from haystack.agents import Agent
agent = Agent(tools=[search_tool, calculator_tool],
prompt_template="Answer questions using the provided tools. Combine results if needed.")
Step 5: Interact with the Agent
Ask your agent questions in natural language:
response = agent.run("Who developed the theory of relativity?")
response = agent.run("What is the result of 8 * (2 + 3)?")
response = agent.run("What is the square root of 16, and who developed it?")
Advanced Features of Haystack Agents
Haystack Agents also offer:
- Custom tools: Integrate specialized APIs for various needs.
- Fine-tuned models: Use models tailored for specific tasks.
- Chained pipelines: Process complex queries from multiple sources.
Conclusion
Haystack Agents provide a robust framework for creating advanced NLP applications that require dynamic reasoning and tool usage. They are excellent for tasks like customer support, educational tools, and business intelligence solutions.
Learn More
For further exploration of Haystack Agents and AI solutions, connect with us via email or follow our social media channels!

























