Understanding Large Language Models (LLMs) in Vehicle Navigation
Large Language Models (LLMs) are sophisticated AI systems designed to understand and generate human-like language by learning from vast amounts of data. As these models become more common in vehicle navigation systems, it’s crucial to evaluate their ability to plan routes effectively.
Recent Developments
In early 2024, many car manufacturers began integrating AI-powered voice assistants into their vehicles. These assistants help with tasks like controlling infotainment, navigation, climate settings, and answering general questions. However, their capability to plan real-world routes needs careful assessment.
Challenges with Traditional Methods
Traditional navigation methods often struggle with memory and efficiency as map data increases. This has led to interest in LLMs, which may offer better solutions. Some studies indicate that LLMs can generate waypoints and assist in Vision-and-Language Navigation (VLN), where robots follow verbal instructions using visual cues. Researchers believe LLMs might outperform standard algorithms like A* in path planning due to their flexibility and creativity.
Research Findings
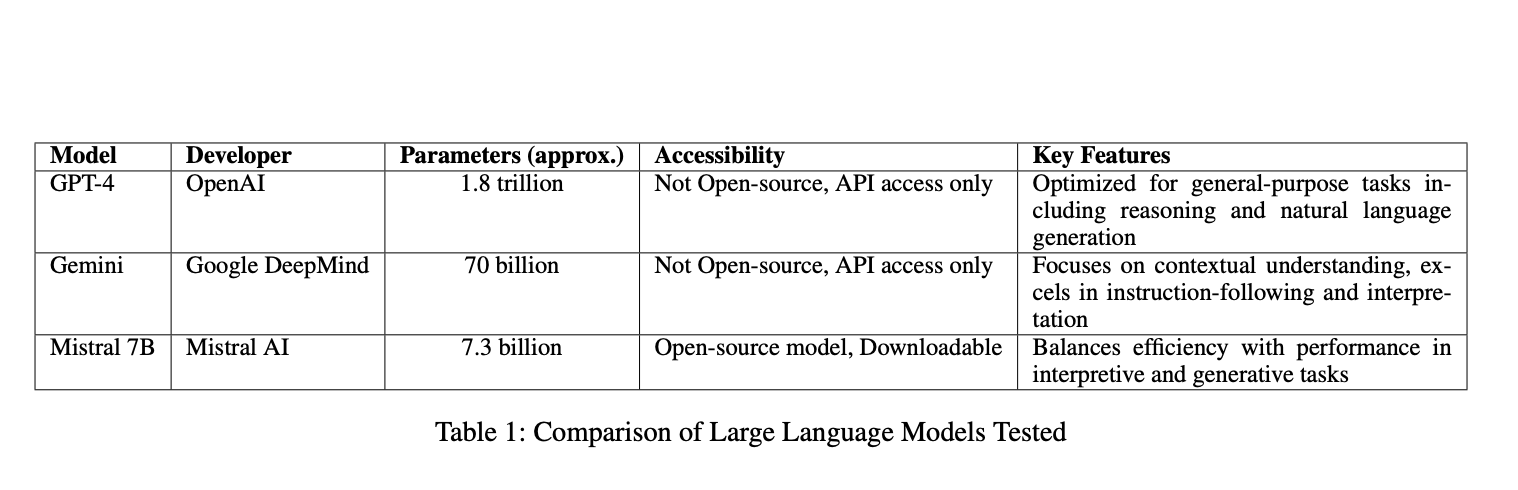
Researchers from Duke University and George Mason University tested three LLMs in six real-world path-planning scenarios of varying difficulty. The study focused on two main tasks:
- Turn-by-Turn (TbT) Navigation: Providing step-by-step directions in different environments.
- Vision-and-Language Navigation (VLN): Guiding users using visual landmarks.
The LLMs tested included GPT-4, Gemini, and Mistral 7B. The study compared their navigation routes to Waze’s data, identifying major and minor errors.
Results of the Study
The findings showed that:
- LLMs often had gaps in routes or provided incorrect directions in TbT navigation.
- In VLN, models struggled with missing segments and wrong landmarks.
- GPT-4 performed best under time constraints, especially in urban settings.
- Mistral excelled in urban navigation, while Gemini was better in VLN.
Overall, none of the models consistently created accurate routes, indicating challenges with spatial understanding.
Conclusion
This research highlights that the tested LLMs are not yet suitable for real-world navigation. While GPT-4 and Gemini showed some strengths, all models made errors. Car manufacturers should be cautious in using these LLMs for navigation. Future work can help develop LLMs specifically designed for this purpose, enhancing vehicle navigation technology.
Stay Connected
Check out the full research paper for more insights. Follow us on Twitter, join our Telegram Channel, and connect with our LinkedIn Group. If you appreciate our work, subscribe to our newsletter and join our 60k+ ML SubReddit community.
Transform Your Business with AI
To stay competitive and leverage AI effectively, consider the following steps:
- Identify Automation Opportunities: Find customer interaction points that can benefit from AI.
- Define KPIs: Ensure measurable impacts on business outcomes.
- Select an AI Solution: Choose tools that fit your needs and allow customization.
- Implement Gradually: Start with a pilot project, gather data, and expand AI usage wisely.
For AI KPI management advice, contact us at hello@itinai.com. For ongoing insights into AI, follow us on Telegram or Twitter.
Discover how AI can enhance your sales processes and customer engagement at itinai.com.



























